ESP Series Microcontrollers
Complete guide to ESP8266 and ESP32 - The powerhouse WiFi/BLE chips for IoT applications

Complete guide to ESP8266 and ESP32 - The powerhouse WiFi/BLE chips for IoT applications

ESP series microcontrollers by Espressif Systems are low-cost, low-power system-on-chips (SoCs) with integrated WiFi and Bluetooth capabilities. They revolutionized IoT development by bringing wireless connectivity to microcontroller projects.
ESP chips come in various development boards and modules. Here are the most popular ESP boards:
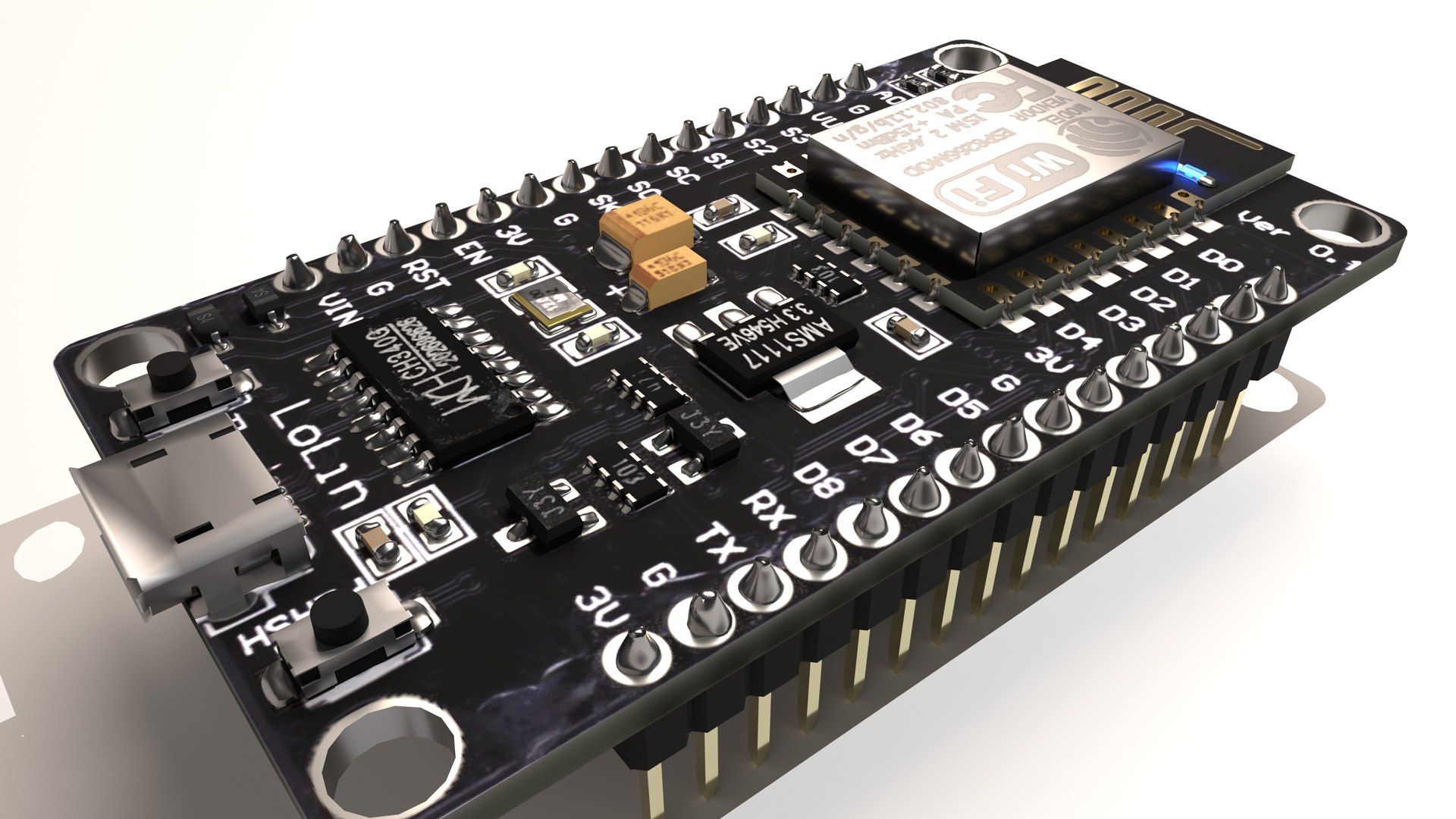
The most popular ESP8266 development board with USB-to-serial
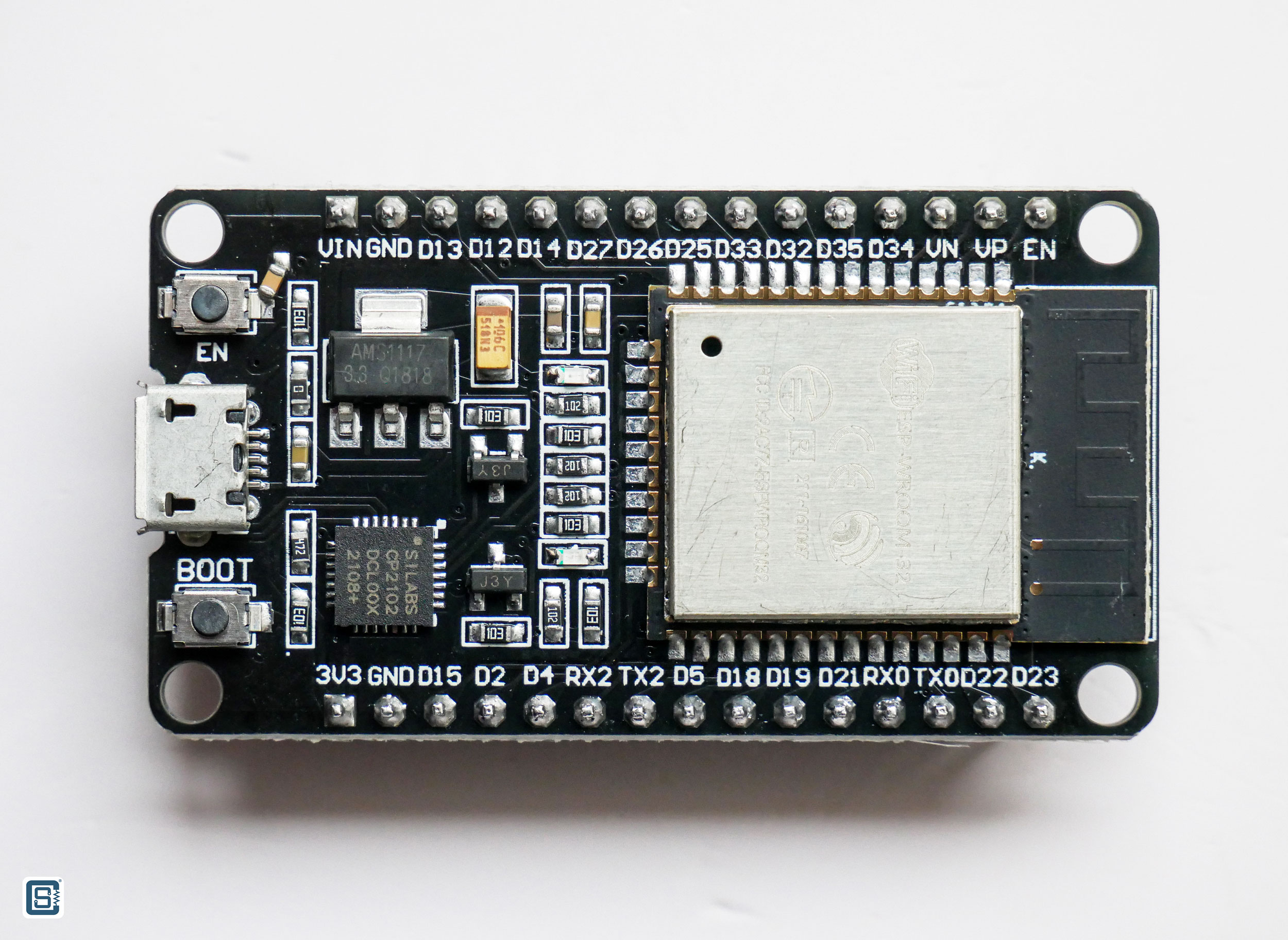
Standard ESP32 development board with full GPIO breakout

ESP32 with OV2640 camera for video streaming

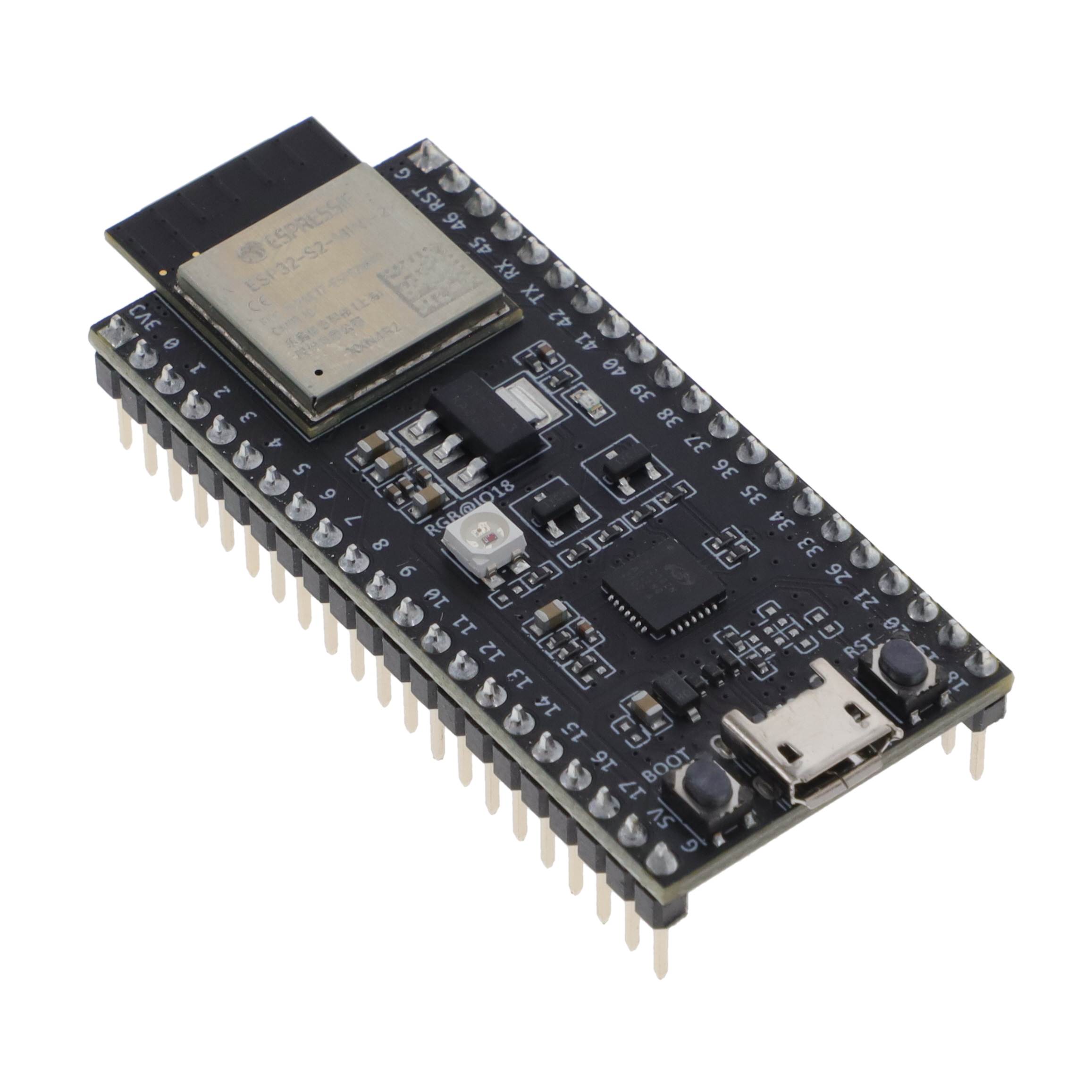
Single-core variant with USB OTG support

RISC-V based chip with WiFi and BLE 5.0
Compare the specifications of different ESP boards:
| Chip/Board | Core | Clock Speed | Wireless | GPIO | Analog | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESP8266 | Xtensa L106 | 80-160MHz | WiFi | 17 | 1 ADC | Low cost |
| ESP32 | Xtensa LX6 (Dual) | 160-240MHz | WiFi + BLE | 36 | 18 ADC, 2 DAC | Touch, Hall, PWM |
| ESP32-S2 | Xtensa LX7 | 240MHz | WiFi | 43 | 20 ADC, 2 DAC | USB OTG |
| ESP32-C3 | RISC-V | 160MHz | WiFi + BLE 5.0 | 22 | 6 ADC | Low power |
| ESP32-S3 | Xtensa LX7 (Dual) | 240MHz | WiFi + BLE 5.0 | 45 | 20 ADC, 2 DAC | AI acceleration |
The NodeMCU is the most popular ESP8266 development board, featuring USB-to-serial conversion and easy breadboard prototyping.
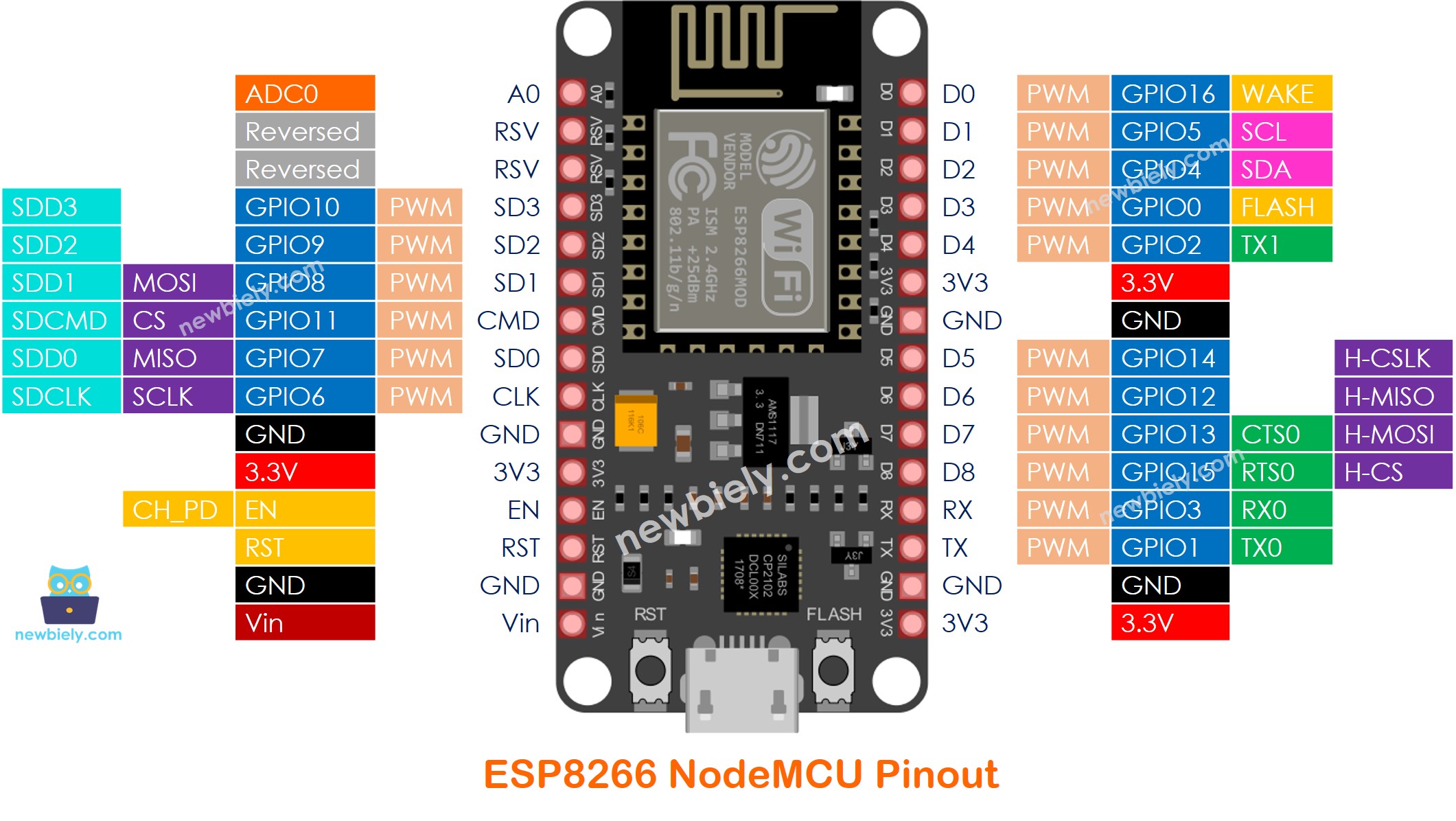
| Pin | Function | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| D0-GPIO16 | Wake from sleep | No interrupt/pullup |
| D1-GPIO5 | I2C SCL | Safe to use |
| D2-GPIO4 | I2C SDA | Safe to use |
| D3-GPIO0 | Boot mode | Pull-up required |
| D4-GPIO2 | TX1, Boot | Connected to onboard LED |
| A0 | Analog Input | 0-3.3V, 10-bit |
NodeMCU can be programmed with Arduino IDE after adding ESP8266 support:
// Simple WiFi Web Server Example
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
const char* ssid = "YourSSID";
const char* password = "YourPassword";
WiFiServer server(80);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
server.begin();
}
void loop() {
WiFiClient client = server.available();
if (client) {
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Hello from NodeMCU!");
client.stop();
}
}ESP32 has two cores that can run tasks simultaneously:
// Run task on Core 0
xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(
Task1, // Task function
"Task1", // Name
10000, // Stack size
NULL, // Parameters
1, // Priority
NULL, // Task handle
0 // Core 0
);
void Task1(void * pvParameters) {
while(1) {
// Your code here
vTaskDelay(1000);
}
}ESP32 includes both classic Bluetooth and BLE:
// Simple BLE Server Example
#include <BLEDevice.h>
BLEServer *pServer;
BLEService *pService;
BLECharacteristic *pCharacteristic;
void setup() {
BLEDevice::init("ESP32_BLE");
pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
pService = pServer->createService("1234");
pCharacteristic = pService->createCharacteristic(
"ABCD",
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_READ |
BLECharacteristic::PROPERTY_WRITE
);
pCharacteristic->setValue("Hello World");
pService->start();
pServer->getAdvertising()->start();
}ESP32 has several power saving modes:
// Deep Sleep Example
#include <esp_sleep.h>
void setup() {
esp_sleep_enable_timer_wakeup(1000000 * 60); // 1 minute
esp_deep_sleep_start();
}
void loop() {} // Never reachedDirect device-to-device communication without WiFi router:
// ESP-NOW Example
#include <esp_now.h>
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status) {
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ?
"Delivery Success" : "Delivery Fail");
}
void setup() {
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("ESP-NOW Init Failed");
return;
}
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress, 6);
peerInfo.channel = 0;
peerInfo.encrypt = false;
esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo);
}